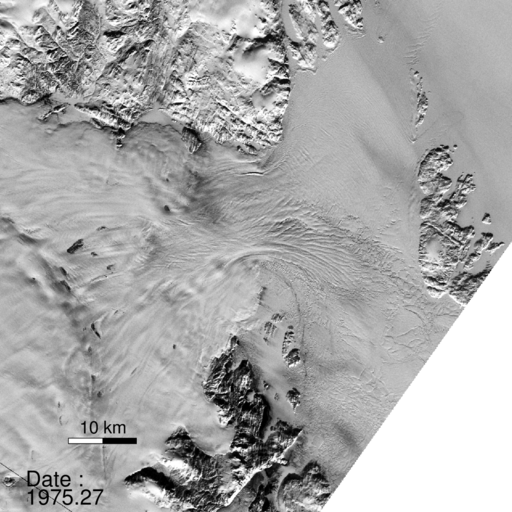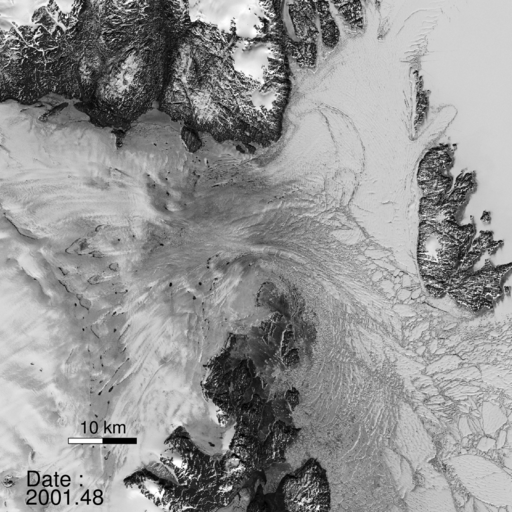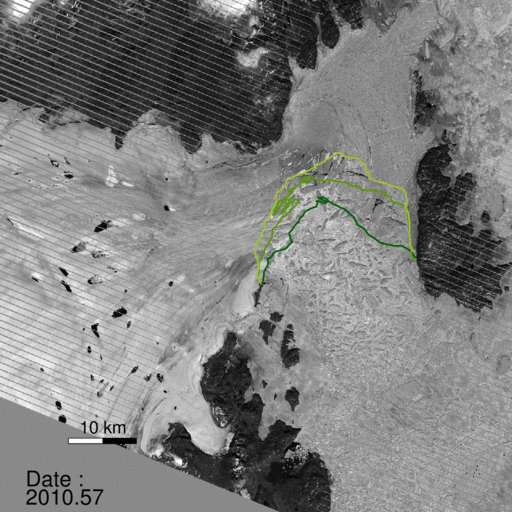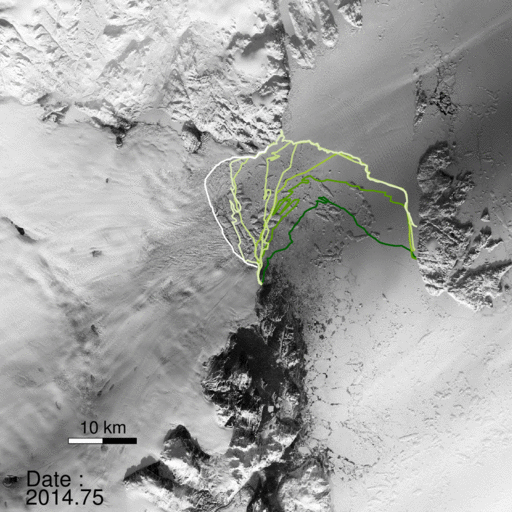
A NASA study published in the journal Science found a glacier in Greenland broke apart. “The consequences will be felt for decades to come.”
“North Greenland glaciers are changing rapidly,” said lead author Jeremie Mouginot, an assistant researcher in the Department of Earth System Science at the University of California, Irvine. “The shape and dynamics of Zachariae Isstrom have changed dramatically over the last few years. The glacier is now breaking up and calving high volumes of icebergs into the ocean, which will result in rising sea levels for decades to come.”
The scientists determined the bottom of Zachariae Isstrom is being rapidly eroded by warmer ocean water mixed with growing amounts of meltwater from the ice sheet surface. “Ocean warming has likely played a major role in triggering [the glacier’s] retreat,” Mouginot said, “but we need more oceanographic observations in this critical sector of Greenland to determine its future.”
“Zachariae Isstrom is being hit from above and below,” said the study’s senior author Eric Rignot, Chancellor’s Professor of Earth system science at UCI, and Joint Faculty Appointee at JPL. “The top of the glacier is melting away as a result of decades of steadily increasing air temperatures, while its underside is compromised by currents carrying warmer ocean water, and the glacier is now breaking away into bits and pieces and retreating into deeper ground.”
“Not long ago, we wondered about the effect on sea levels if Earth’s major glaciers in the polar regions were to start retreating,” Rignot noted. “We no longer need to wonder; for a couple of decades now, we’ve been able to directly observe the results of climate warming on polar glaciers. The changes are staggering and are now affecting the four corners of Greenland.”